Introduction
Your brand just lost 18% of its profit margins. Not because of a bad quarter or rising costs — but because retailers quietly advertised your products below the prices you agreed on.
This is the reality of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violations in 2026. With nearly 40% of consumers willing to switch retailers for better deals, even a single rogue discount can trigger a race to the bottom. Your premium positioning erodes. Your compliant retailers lose motivation. And your carefully built brand perception takes a hit that's hard to reverse.
The challenge? Monitoring prices across hundreds of resellers, marketplaces, and regional storefronts is practically impossible without automation. That's where MAP monitoring software — powered by web scraping and AI — becomes essential infrastructure for any brand serious about protecting its value.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about MAP monitoring in 2026: what it is, why it matters more than ever, and how to implement automated systems that catch violations before they damage your business.
What is MAP Monitoring?
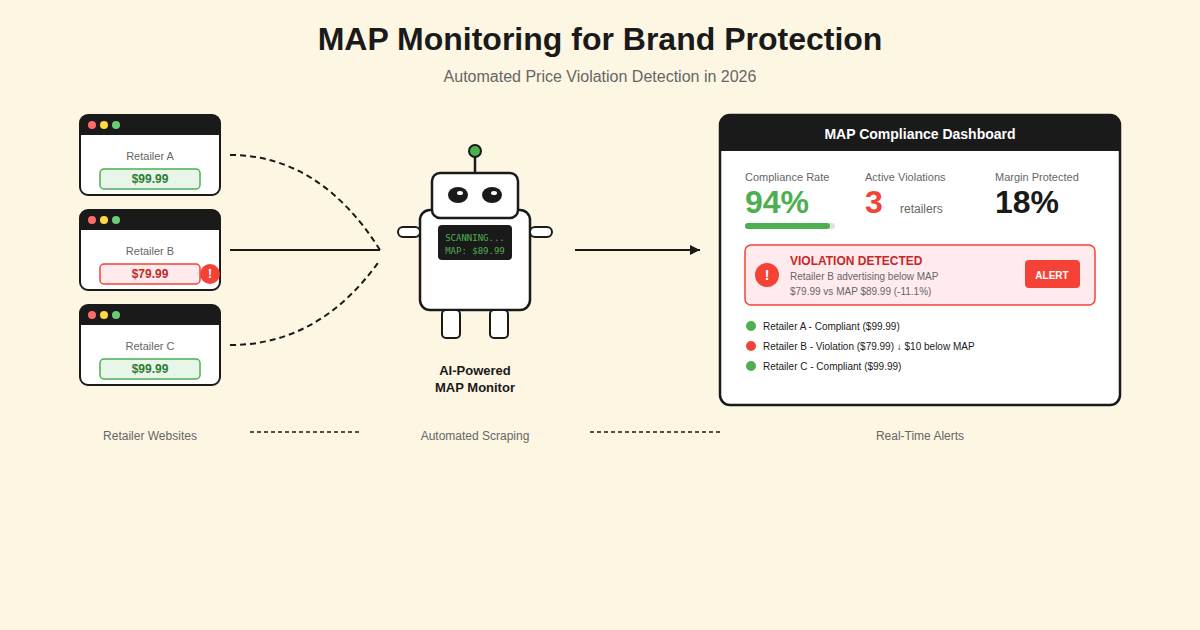
MAP monitoring is the automated process of tracking advertised prices across all your sales channels to ensure retailers comply with your Minimum Advertised Price policy.
A MAP policy sets the lowest price a retailer can publicly advertise your product — not the price they ultimately sell it for. Retailers can still offer lower prices at checkout, but they cannot display those prices in product listings, Google Shopping feeds, email campaigns, or any public-facing marketing.
The distinction matters legally. In the United States, MAP policies remain legal under federal antitrust laws because they restrict advertising, not actual resale prices. However, enforcement is entirely your responsibility. Without active monitoring, even well-intentioned retailers drift below MAP under competitive pressure, and unauthorized sellers undercut everyone.
Modern MAP monitoring systems work by continuously scraping product listings across authorized retailers, marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, Google Shopping feeds, and even social media ads. They match products using SKUs, GTINs, or AI-powered product recognition, then flag any advertised price that falls below your defined threshold.
Why MAP Compliance Matters More in 2026
The e-commerce landscape has shifted dramatically. Three forces make MAP enforcement more critical — and more difficult — than ever before.
Price transparency is absolute. Comparison shopping tools, browser extensions like Honey, and AI shopping assistants surface every price difference instantly. One retailer advertising below MAP doesn't just capture sales — they make your compliant partners look overpriced. According to Priceva's MAP monitoring data, about 30% of tracked products show serious MAP deviations daily, resulting in an average 18% loss in profit margins for affected brands.
Marketplaces have multiplied. Your products now appear on Amazon, eBay, Walmart Marketplace, regional platforms, social commerce, and countless niche retailers. Manual price checking across this ecosystem is impossible. The price monitoring software market itself is projected to reach $2.17 billion by 2026, reflecting how seriously brands take automated price intelligence.
Anti-bot defenses have intensified. Ironically, the same protections that make websites harder to scrape also make it harder for brands to monitor their own pricing. Sites use sophisticated fingerprinting, behavior analysis, and real-time traffic monitoring to detect automated access. This means DIY monitoring scripts break constantly, and brands need professional-grade scraping infrastructure to maintain visibility.
For brands that sell through distributors, MAP violations aren't just about lost margin. They signal to compliant retailers that playing by the rules puts them at a disadvantage. Over time, this erodes channel relationships and can push reliable partners toward competitors who enforce their policies.
How Automated MAP Monitoring Works
Effective MAP monitoring combines web scraping, product matching, and alert systems into a continuous compliance workflow. Here's what happens behind the scenes.
Data collection begins with automated scrapers that visit retailer websites, marketplace listings, and advertising platforms on a scheduled basis — often daily or even hourly for fast-moving categories. These scrapers must handle JavaScript-rendered pages, login walls, regional pricing differences, and anti-bot protections. Platforms like ScrapeWise use AI-powered extraction that adapts automatically when websites change their layouts, eliminating the maintenance burden that breaks traditional scraping approaches.
Product matching identifies your specific SKUs across different retailers, even when product titles, images, or descriptions vary. This typically uses a combination of GTIN/UPC matching, SKU lookup, and increasingly, AI-based product recognition that can match products visually or semantically.
Violation detection compares collected prices against your MAP thresholds. Good systems distinguish between the advertised price and promotional tactics like "see price in cart" that may or may not violate your policy depending on how it's structured. They also capture screenshots as evidence for enforcement actions.
Alerting and reporting notify your team immediately when violations occur. The best platforms prioritize alerts by severity — distinguishing a $5 deviation from a catastrophic 40% discount — and provide historical data to identify repeat offenders versus one-time errors.
Enforcement integration connects monitoring data to your compliance workflow, whether that's automated warning emails, CRM updates, or documentation for legal action against unauthorized sellers.
Common MAP Violation Tactics to Watch
Retailers have developed sophisticated methods to advertise below MAP without appearing to violate the letter of your policy. Your monitoring system needs to catch these tactics.
"See price in cart" or "Add to cart for price" hides the actual price until the customer takes an action. Whether this constitutes a MAP violation depends on your policy language. Recent case law suggests that prices displayed within shopping carts may fall outside MAP protection, making clear policy definitions essential.
Bundle pricing combines your product with accessories or services at a "discount" that effectively prices your item below MAP. Monitoring systems need to identify when your products appear in bundles and calculate the implied individual price.
Coupon stacking layers multiple promotional codes to reach below-MAP prices. While the base advertised price may be compliant, the effective price after applying readily available coupons might not be.
Time-limited flash sales drop prices briefly, hoping the violation goes undetected before monitoring catches it. This is why daily or hourly monitoring matters more than weekly spot-checks.
Regional or international arbitrage exploits different MAP thresholds across markets. A product might be compliant in one country but violate policy when resold into another market through gray-market channels.
Building Your MAP Monitoring Stack
For brands serious about MAP compliance, the monitoring stack typically includes several components.
Web scraping infrastructure forms the foundation. This can be an in-house solution using tools like Scrapy or Playwright, a managed scraping service, or a purpose-built competitive price monitoring platform. The key requirements are reliability across diverse websites, automatic adaptation to site changes, and compliance with rate limits to avoid being blocked.
Product data management maintains your master catalog with SKUs, GTINs, MAP prices by region, and any promotional periods where different thresholds apply. This needs to integrate with your monitoring system so price comparisons are always current.
Alert and workflow management routes violations to the right team members and tracks resolution status. Many brands integrate this with existing CRM or ticketing systems rather than managing it separately.
Evidence capture stores screenshots, timestamps, and price history for each violation. This documentation is essential for enforcement conversations and potential legal action against unauthorized sellers.
Reporting and analytics reveal patterns over time: which retailers violate most frequently, which products are most affected, seasonal trends, and the financial impact of violations.
Best Practices for MAP Enforcement
Monitoring without enforcement is just expensive observation. Here's how brands with strong MAP programs approach compliance.
Communicate proactively. Before violations occur, ensure every authorized retailer understands your MAP policy, the monitoring you conduct, and the consequences of violation. Many violations stem from ignorance or systems errors rather than intentional undercutting.
Enforce consistently. Apply the same standards and penalties to all retailers, regardless of their size or importance to your business. Inconsistent enforcement exposes you to legal risk and breeds resentment among compliant partners. Use standardized violation workflows with clear escalation timelines.
Escalate progressively. Start with a formal warning that identifies the specific violation and requests immediate correction. Second violations might trigger a 30 or 60-day product suspension. Third violations could mean termination of the authorized relationship. Document everything.
Prioritize by impact. Not all violations are equal. A major retailer advertising 20% below MAP damages your brand far more than a small reseller making a $2 error. Focus enforcement resources where they protect the most value.
Address unauthorized sellers separately. You cannot enforce MAP against sellers who never agreed to your policy. However, you can pursue other remedies: trademark claims, complaints to marketplace platforms, and cutting off their supply by identifying which distributors are leaking product.
The ROI of MAP Monitoring
The business case for automated MAP monitoring is straightforward when you quantify what violations cost.
Direct margin loss occurs when compliant retailers match violator prices to stay competitive. If your MAP exists to protect a 30% margin and violations push street prices down 15%, you've lost half your margin across every sale.
Channel conflict erodes relationships with partners who follow the rules. When they see competitors gaining advantage through violations you don't address, they question whether compliance benefits them. Some may leave for brands that enforce better; others may start violating themselves.
Brand perception damage accumulates subtly. When consumers consistently find your "premium" products discounted below list price, they question whether the premium positioning is real. This affects willingness to pay across all channels, including direct sales.
Enforcement cost without monitoring is prohibitively high. Manual price checking across even a modest distribution network takes dedicated staff time that grows linearly with your catalog size and channel count. Automated monitoring scales far more efficiently.
Brands that implement comprehensive MAP monitoring typically report margin recovery that far exceeds the cost of monitoring tools. The 18% margin loss associated with uncontrolled violations represents an enormous opportunity for brands that take enforcement seriously.
Conclusion
MAP violations are not a minor inconvenience — they're a systematic threat to brand value, channel relationships, and profit margins. In 2026, with price transparency at an all-time high and consumers switching retailers for the smallest discount, brands cannot afford to monitor manually or enforce inconsistently.
The technology exists to automate this entire workflow. AI-powered scraping adapts to website changes without constant maintenance. Product matching works across marketplaces with different naming conventions. Alert systems notify you within hours of violations, not days.
For brands ready to take MAP enforcement seriously, platforms like ScrapeWise offer purpose-built infrastructure for competitive price monitoring that scales with your catalog and distribution network.
The question isn't whether to invest in MAP monitoring. It's how much margin you're willing to lose while you wait.